Unveiling Mobile App Vulnerabilities: How Popular Apps Leak Sensitive Data
A look at eight Android and iOS apps that fail to protect sensitive user data.
In an increasingly digital world, the importance of mobile security cannot be overstated. With millions of apps available on Google’s Play Store and Apple’s App Store, users trust developers to safeguard their personal information. Unfortunately, this trust is often misplaced.
A key step in preventing unauthorized access to user data is encryption, especially when it comes to moving data from device to server and back again. If implemented incorrectly by app developers, it can expose users to a host of potential attack scenarios, including data theft, eavesdropping, and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, just to name a few.
Many apps analyzed by Symantec transmit unencrypted user data over the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS, exposing the information to anyone monitoring the session. In this blog, we detail just eight of these apps, which were found to transmit sensitive unencrypted data, including device information, geo-location, and credentials.
App Analysis
Klara Weather (Android)
Download count: Over 1 million on the Google Play Store
Issue: Sends location unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 1) and code inspection (Figure. 2) reveal that user geolocation is leaked through unencrypted HTTP traffic.


Military Dating App - MD Date (iOS)
Rating count: 17,700 on the Apple App Store
Issue: Sends credentials unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 3) and code inspection (Figure. 4) show usernames and passwords transmitted via unencrypted HTTP traffic.
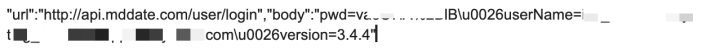

Sina Finance (Android)
Download count: Over 100,000 on the Google Play Store
Issue: Sends device information unencrypted
Details: Analysis of network traffic (Figure. 5) and code (Figure. 6) indicate that device information, including device ID, SDK version, and IMEI, is leaked through unencrypted HTTP traffic.


CP Plus Intelli Serve (Android)
Download count: Over 50,000 on the Google Play Store
Issue: Sends credentials unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 7) and code inspection (Figure. 8) reveal that usernames and passwords are transmitted unencrypted.

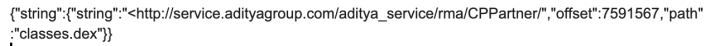
Latvijas Pasts (Android)
Download count: Over 100,000 on the Google Play Store
Issue: Sends location unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 9) and code inspection (Figure. 10) show that user geolocation is leaked through unencrypted HTTP traffic.

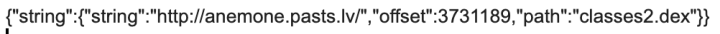
HaloVPN: Fast Secure VPN Proxy (iOS)
Rating count: 13,300 on the Apple App Store
Issue: Sends device information unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 11) and code inspection (Figure. 12) indicate that device information, including device ID, language, model, name, time zone, and SIM information, is leaked through unencrypted HTTP traffic.


i-Boating: Marine Charts & GPS (iOS)
Rating count: 11,600 on the Apple App Store
Issue: Sends device information unencrypted
Details: Analysis of network traffic (Figure. 13) and code (Figure. 14) show that device information, such as device type and OS version, is transmitted unencrypted.


Texas Storm Chasers (iOS)
Rating count: 9,200 on the Apple App Store
Issue: Sends location unencrypted
Details: Network traffic analysis (Figure. 15) and code inspection (Figure. 16) reveal that user geolocation is transmitted via unencrypted HTTP traffic.


A Continuing Problem
App developers have a duty of care to the people who use their apps; however, as we have seen with these examples, whether intentional or an oversight, many developers fail to protect sensitive user data by transmitting it unencrypted. This not only breaches user trust but also exposes users to significant risks, including identity theft, unauthorized access, and data breaches. This issue is not a new one and, unfortunately, has been commonplace for far too long.
Mobile app security is a critical concern that developers must prioritize. App developers can avoiding security risks such as those highlighted in this blog by adhering to the following best practices:
- Use HTTPS for all network traffic:
- Ensure all data transmission between the app and the server is encrypted using HTTPS.
- Encrypt sensitive data:
- Use strong encryption methods to protect sensitive information, such as user credentials and location data, both in transit and at rest.
- Regular security audits:
- Conduct regular code reviews and security audits to identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities.
As users, we must remain vigilant and demand higher security standards from app developers. By being aware of the security practices of the apps we use, we can make informed choices and protect our personal information.
All of the organizations whose vulnerable apps were discussed in this blog have been notified about the issues we uncovered.
Protection/Mitigation
For the latest protection updates, please visit the Symantec Protection Bulletin.
Symantec recommends users follow these best practices to stay protected from mobile threats:
- Install a suitable security app, such as Symantec Endpoint Protection, to protect your device and data
- Refrain from downloading apps from unfamiliar sites and only install apps from trusted sources
- Keep your software up to date
- Pay close attention to the permissions that apps request
- Make frequent backups of important data







We encourage you to share your thoughts on your favorite social platform.