Symantec Mobile Threat Defense: Spotlight on Modern Endpoint Vulnerability Management
The age-old practice of vulnerability management to mitigate security risks can (and should) extend to modern endpoints
Just because you can’t see something doesn’t mean it’s not there. This popular refrain is perhaps nowhere more evident and telling than in mobile security. One of the consistent challenges facing enterprise security teams today is lack of visibility over their mobile threat landscape, which includes malware, network threats, app risks and operating system (OS) vulnerabilities. This article will deep-dive into the latter, a growing pain point for enterprises.
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure (CVE) program identifies hundreds of mobile OS vulnerabilities each year, some of them critical. Apple and Google release security updates/patch levels on a monthly basis, but mobile users aren’t always aware of the updates; even when they are, they don’t always install them, and even if they want to install them, updates are not always available for their device. In many cases, vulnerabilities remain open for exploitation because security teams are not aware of them early on enough or don’t have the tools to respond. What can organizations do to stay on top of these risks and mitigate them?
Borrowing a Page from Traditional Endpoint Security
In network and traditional endpoint security programs, admins have used the longstanding practice of vulnerability management to identify, prioritize, and remediate software vulnerabilities. Among other benefits, vulnerability management provides the core ability to see all the known vulnerabilities, and their severity, that an organization is exposed to. Once there is a clearer picture of the vulnerability landscape, admins can prioritize and respond to the risk in a variety of ways, such as installing a security patch (remediation) or removing the vulnerable system from the network (mitigation).
Just as vulnerability management has become a core component of endpoint security programs, so too should it be used in mobile security. After all, a mobile endpoint is an endpoint, making mobile security an integral part of endpoint security. Enterprise security programs that do not extend vulnerability management to mobile basically assume that mobile devices are not susceptible to the OS vulnerabilities that threaten traditional endpoints. We know that’s not the case.
Ultimately, every operating system is vulnerable to risk. On mobile, the risk is even expanded: mobile devices are always on, they are always connected, and users behave less securely on them (connecting to more networks freely, downloading apps that may be risky, heavily using email and instant-messaging apps, etc.) It takes just one exploitation of an OS vulnerability to give an attacker full access to a device’s content, to the networks it connects to, and to the cloud and on-prem business systems it accesses. Furthermore, hackers can get access to a device’s sensors, allowing them to spy on victims 24/7 without them knowing. The premise is clear: if admins use vulnerability management to reduce the risk of software exploits in Windows or Mac endpoints, they should unquestioningly be using it to reduce the risk of exploits on Android and iOS devices.
Vulnerability Management for Mobile
The problem is that vulnerability management programs do not have the same oversight and control over the wild west of mobile, as they do over traditional endpoints. In mobile, it is the end-users (and often the mobile carrier or manufacturer they are using) – not IT – who decide which firmware to use and whether/when to install security updates. IT admins can’t conduct active vulnerability assessments on mobile devices and they can’t force security updates/patches.
Symantec bridges this gap by providing mobile vulnerability management as part of our enterprise mobile threat defense solution, Symantec Endpoint Protection Mobile (SEP Mobile). SEP Mobile’s vulnerability management detects known OS vulnerabilities on both managed and unmanaged mobile devices in an organization. Together with its mobile endpoint detection and response (EDR) technology, it allows admins to identify and collect forensics on vulnerability exploitation (a topic we’ll delve into in an upcoming blog post).
As in traditional vulnerability management programs, SEP Mobile’s data on CVEs and their risk comes in large part from MITRE, the entity responsible for maintaining the CVE database, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which gives CVEs their Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). However, in light of MITRE’s limited ability in recent years to keep up with new CVE's and their risk assessment, SEP Mobile also monitors ongoing security updates published by Apple and Google on iOS and Android CVEs, respectively, and assigns them a risk level. All of this data is used to properly assess vulnerabilities and prioritize response.
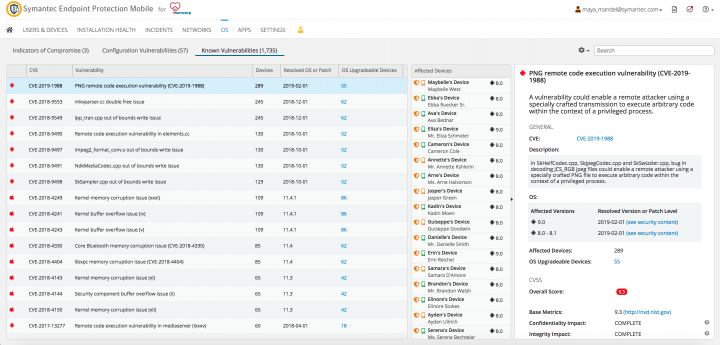
Essentially, SEP Mobile turns the light on an otherwise dark mobile CVE landscape, enabling admins to know which devices are exposed to risk, what the risks are, how severe they are, and how they can be remediated.
Visibility is Crucial but it’s Not Enough
Our discussion at the beginning of the article raised the question of how organizations can protect themselves against mobile vulnerabilities if they don’t know about them. Vulnerability management can provide much-needed visibility over the mobile CVE landscape but seeing is not enough. Visibility without risk assessment and actionability only does part of the job for admins, leaving them to do the guesswork about which vulnerabilities to respond to and how. Worse, solutions that only detect vulnerabilities without offering further action may impact productivity by creating information overload and cyber fatigue.
Effective mobile endpoint vulnerability management delivers continuous risk reduction by detecting vulnerabilities, assessing their severity, and providing insights and tools that can help admins remediate risks.
Beyond monitoring for known mobile vulnerabilities and giving context about their potential harm, SEP Mobile’s vulnerability management system provides insights and severity ratings for each new vulnerability, as well as the ability to ensure employees are upgrading their OSs in accordance with the organization’s mobile security policy.
The importance of each of these benefits is discussed below.
CVE Risk Rating
Mobile has become a more attractive attack vector for hackers in recent years, as evidenced by the growing number of mobile-related CVEs. In fact, Android and iOS are reported to be among the top five most vulnerable operating systems (excluding applications) in the market. To make matters worse, MITRE has struggled over the last few years to keep up with the number of CVEs. Consequently, the NVD, which gives CVEs their CVSS score, has not been able to provide timely CVE risk assessments, with researchers sometimes having to wait for several months to get a risk score. This has resulted in a black hole for organizations relying on this information to determine their mobile risk.
SEP Mobile fills this vacuum by assigning every new vulnerability a risk severity rating. Using machine learning, the SEP Mobile research team trained a model to classify the severity of new vulnerabilities. In the absence of a CVSS score, the severity rating is provided to help admins understand the risk of vulnerabilities in their environment, without having to wait for the NVD’s assessment.
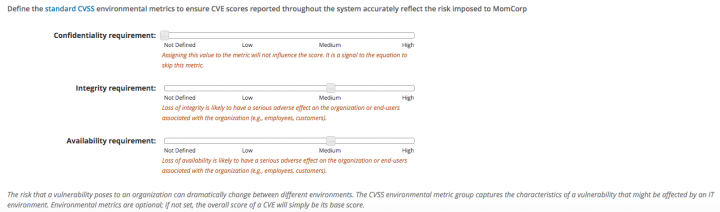
SEP Mobile’s insights and severity rating can be leveraged by admins to make better decisions on vulnerability prioritization and response. Additionally, as different organizations weigh vulnerabilities differently, SEP Mobile provides built-in functionality that enables admins to define the environmental metrics that impact the CVSS score in accordance with an organization’s IT environment. This allows CVSS scores to accurately reflect the risk posed to a specific environment.
Actionability: Mitigating Your Risk Levels
SEP Mobile allows organizations to decide exactly how tolerant they want to be to outdated OS versions or security patch levels, by defining certain rules in their mobile security compliance policy.
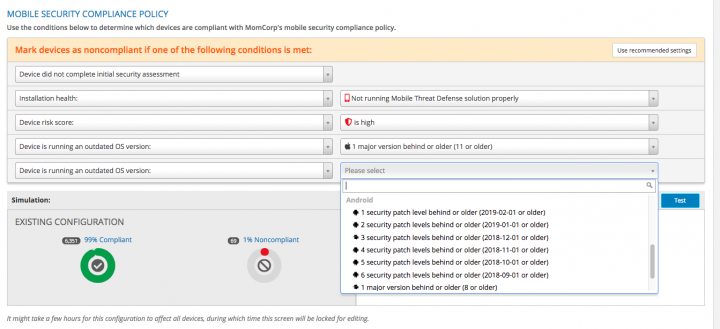
Security teams can mitigate the risk of CVE exploitation by setting a policy on how many patch levels or versions back the organization allows its mobile devices to run before they are considered non-compliant. This security compliance policy enables admins to enforce OS version or patch level upgrades on both managed and unmanaged non-compliant endpoints. Devices that are not compliant are blocked from accessing sensitive corporate resources until the end-user upgrades to a current OS version or patch level that corrects the risk and adheres to the corporate policy. Before creating a rule and blocking resource access, admins can use built-in policy simulation tools to see how much of their user base will be impacted. In cases where a high number of devices would be affected, the organization can decide to take measures urging users to upgrade (i.e. education, communication, etc.)
No less important, SEP Mobile allows security teams to take proactive action to ensure devices are running the latest OS, by:
- Leveraging unprecedented upgradeability information.
- Notifying users as soon as a new version/patch level is available.
In the management console, admins can see the latest OS versions available for iOS and Android devices, as well as the latest Android security patch level. On Android in particular, different mobile phone vendors and carriers implement upgradeability differently, based on parameters such as the manufacturer, device model, OS & patch level, as well as different carrier procedures. Taking this complex upgradeability landscape into account, SEP Mobile uses a unique combination of proprietary algorithms and crowd wisdom to tell admins exactly which devices should upgrade to which patch levels and when.
On top of this, admins can use SEP Mobile to automate push notifications and emails alerting end-users about a new version/patch level when it is available. In most cases, SEP Mobile notifies users about the availability of an upgrade even before the OS vendor itself sends a push notification to the device. SEP Mobile’s communication options also enable admins to notify end users when their device is non-compliant due to outdated OS versions. In cases where organizations understand the risks but prefer that their mobile users don’t upgrade, admins can choose not to send alerts.
Get on the Mobile Vulnerability Management Bandwagon
Security professionals can no longer convince themselves that unseen vulnerabilities are not there. The risk from mobile threats is growing and, just as organizations use vulnerability management to protect their traditional endpoints from software exploits, they would do well to use it for their modern endpoints. Mobile vulnerability management tools can provide visibility on known vulnerabilities affecting iOS and Android devices, but tools that also provide risk assessment and actionable insights will be most effective in ensuring continuous risk reduction. With SEP Mobile’s vulnerability management, admins don’t need to break a sweat trying to figure out which vulnerabilities pose the highest risk and how to respond to them – SEP Mobile does this work, providing organizations all the tools they need to reduce mobile risk.








We encourage you to share your thoughts on your favorite social platform.