SolarWinds Attacks: Stealthy Attackers Attempted To Evade Detection
In the first of a series of follow-up analysis on the SolarWinds attacks, we take a look at how the attackers disabled security software and avoided detection
As we continue our analysis on the tools used in the SolarWinds attacks, one of the most striking aspects we’ve noticed is how careful the attackers were to avoid drawing attention to themselves. Software supply chain attacks are relatively stealthy to begin with, since signed software from a trusted source is less likely to raise red flags. However, the attackers weren’t content to rely on the cover this provided and also took several other steps to avoid detection.
To begin with, the Sunburst backdoor (Backdoor.Sunburst), which was delivered using a Trojanized update to SolarWinds Orion, sets a delay time of up to 14 days before execution. In other words, no malicious activity will begin until this period has elapsed.
The length of time selected is most likely to increase the likelihood that the log entries of the initial malicious activity have been deleted before any subsequent post-breach activity is initiated, thereby making it difficult to correlate the two sets of malicious events. Many organizations, including even managed security services providers (MSSPs), will often purge their security logs after seven days to minimize storage costs and make searching them easier.
Sunburst will also check the current Windows domain the machine belongs to. If the domain contains the string 'test' or one of 13 additional specific domains that appear related to lab systems such as “swdev.local” and “apac.lab”, the threat will cease to execute. A full list is in Appendix A.
Avoiding Security Software and Researchers
Attacks begin with a Trojanized version of SolarWinds’ Orion software. The attackers modified Orion in order to deliver the Sunburst backdoor to the computer. Sunburst is first stage malware, designed to perform reconnaissance on the infected computer, perform checks for security tools, and deliver a second stage payload, if required.
The main Sunburst code is contained in a class named SolarWindows.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer that, when first instantiated, calls a member function called Update. The function name is a ruse, as the code does not perform any update, but instead is designed to disable security software, avoid security researcher systems, and possibly avoid running on systems not of interest to the attackers. The function contains three lists – a list of process names, a list of driver filenames, and a list of processes and service name pairs. These names are all obfuscated in the code by hashing them using the FNV1A algorithm and using variable names that masquerade as timestamps.
The function will:
- Get a list of running processes.
- Check if the process names match items on the process list
- Get a list of all installed drivers
- Check if the driver names match items on the drivers list
- If a match is found, the malicious code does not perform further actions and returns
This process and driver list contains tools that commonly run on security researcher systems and thus, this functionality appears to be designed not to run on such systems in order to avoid discovery. The full list of security tools can be found in Appendix A. Furthermore, the lists also contained names related to a variety of security software programs including:
- Security software process names
- AVG/AVAST
- Panda
- Kaspersky
- Tanium
- Driver names
- CyberArk - cybkerneltracker.sys
- Altiris Symantec - atrsdfw.sys (Ghost Pre-installation boot environment driver)
- Raytheon Cyber Solutions - eaw.sys
- CJSC Returnil Software - rvsavd.sys
- Verasys Digital Guardian - dgdmk.sys
- Sentinel One – sentinelmonitor.sys
- Hexis Cyber Solutions - hexisfsmonitor.sys
- Dell SecureWorks - groundling32.sys, groundling64.sys
- SAFE-Cyberdefense - safe-agent.sys
- Cybereason – crexecprev.sys
- Absolute - psepfilter.sys, cve.sys
- Bromium - brfilter.sys, brcow_x_x_x_x.sys
- LogRhythm - lragentmf.sys
- OESIS OPSwat - libwamf.sys
The security vendors on this list have most likely been chosen as the attacker has determined that their products are unlikely be installed at organizations of interest to the attackers. Given the indiscriminate nature of supply chain as a vector, with an estimated 18,000 SolarWinds customers affected, the attackers probably wanted to avoid any risk of detection in organizations that weren’t of interest to them.
Interestingly, the process solarwindsdiagnostics is also blacklisted. Presumably this is included to avoid detection during any SolarWinds testing or troubleshooting.
Disabling security software
Sunburst also attempts to specifically disable some software security services via the registry. This allows Sunburst to perform its malicious actions completely undetected. If the attackers worked quickly and restored the services afterwards, a security administrator would potentially have no record of the activity, nor have even noticed the temporary lack of protection.
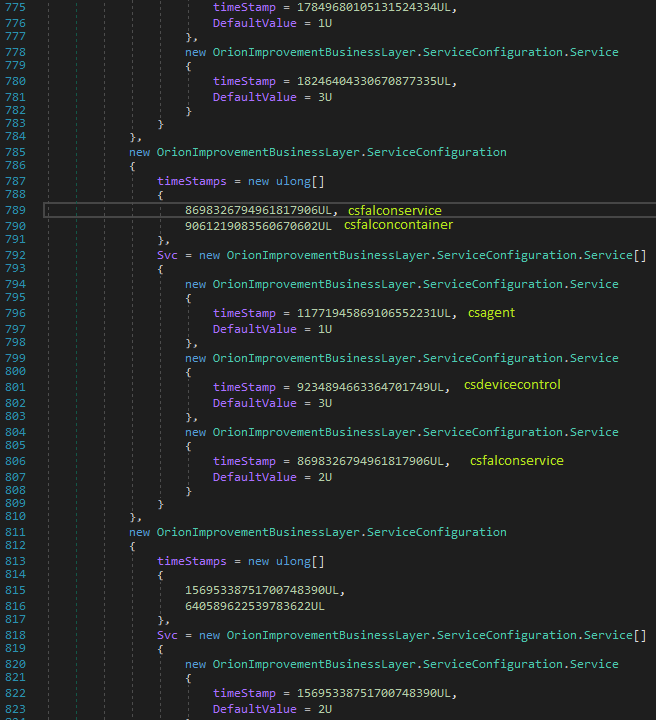
Figure 1. Example of how Sunburst disables security software. In this case it checks if the CrowdStrike processes csfalconservice or csfalconcontainer are running, and if so, it sets the csagent, csfalconservice, and csdevicecontrol services to be disabled.
This function will:
- Get a list of running processes
- Check if the process names match items on the process/services name pair list
- Disable the security software by modifying its service registry entry
- After the software has been confirmed to be disabled, usually after a reboot, the malicious code will then contact the command and control (C&C) server and potentially perform further malicious actions
To disable the security software, Sunburst will simply set the products’ service start setting to Disabled. In Windows, this is done by setting the registry keys:
- HKLM\ SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\<service name>\Start = 4
This will cause the security software not to load at the next reboot.
It should be noted that the attackers do not attempt to disable any Symantec products. Presumably this is because of an anti-tampering feature in Symantec software, which prevents its own service from being disabled.
The process and services pair list include software from the following vendors:
- CrowdStrike
- Carbon Black
- FireEye
- ESET
- F-Secure
Interestingly, the list also included Microsoft Defender, but only the service key permissions are changed. Currently, this has an unknown effect. In addition, some other unknown products are also included, but were effectively commented out. The attackers may have discovered this technique was ineffective for these products.
Finally, Sunburst will check if api.solarwinds.com resolves to a valid address before continuing.
Low profile threat
The SolarWinds attacks are among the best-planned and adept attacks we have seen in recent years. The attackers have gone to great lengths to both find an effective path into their targeted organizations and, once inside their networks, maintain a low profile. Our analysis of these tools is ongoing and we plan to publish further blogs in the coming weeks.
Protection/Mitigation
Tools associated with these attacks will be detected and blocked on machines running Symantec Endpoint products.
File-based protection:
- Backdoor.Sunburst
- Backdoor.Sunburst!gen1
- Backdoor.SuperNova
- Backdoor.Teardrop
Network-based protection:
- System Infected: Sunburst Malware Activity
Appendix A
Drivers Avoided
| Driver | FNV1A Hash | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ybkerneltracker.sys | 17097380490166623672 | |
| atrsdfw.sys | 15194901817027173566 | Altiris Symantec (Ghost Preinstallion boot environment driver) |
| eaw.sys | 12718416789200275332 | Raytheon Cyber Solutions |
| rvsavd.sys | 18392881921099771407 | CJSC Returnil Software |
| dgdmk.sys | 3626142665768487764 | Verdasys |
| sentinelmonitor.sys | 12343334044036541897 | Sentinel |
| hexisfsmonitor.sys | 397780960855462669 | Sentinel One |
| groundling32.sys | 6943102301517884811 | Dell SecureWorks |
| groundling64.sys | 13544031715334011032 | Dell SecureWorks |
| safe-agent.sys | 11801746708619571308 | SAFE-Cyberdefense |
| crexecprev.sys | 18159703063075866524 | Absolute (Palisade Systems) |
| psepfilter.sys | 835151375515278827 | Absolute |
| cve.sys | 16570804352575357627 | Absolute |
| brfilter.sys | 1614465773938842903 | Bromium |
| brcow_x_x_x_x.sys | 12679195163651834776 | Bromium |
| lragentmf.sys | 2717025511528702475 | LogRhythm |
| libwamf.sys | 17984632978012874803 | OESIS OPSwat |
Security Tools Avoided
| Tool | FNV1A Hash |
|---|---|
| apimonitor-x64 | 2597124982561782591 |
| apimonitor-x86 | 2600364143812063535 |
| autopsy64 | 13464308873961738403 |
| autopsy | 4821863173800309721 |
| autoruns64 | 12969190449276002545 |
| autoruns | 3320026265773918739 |
| autorunsc64 | 12094027092655598256 |
| autorunsc | 10657751674541025650 |
| binaryninja | 11913842725949116895 |
| blacklight | 5449730069165757263 |
| cff explorer | 292198192373389586 |
| cutter | 12790084614253405985 |
| de4dot | 5219431737322569038 |
| debugview | 15535773470978271326 |
| diskmon | 7810436520414958497 |
| dnsd | 13316211011159594063 |
| dnspy | 13825071784440082496 |
| dotpeek32 | 14480775929210717493 |
| dotpeek64 | 14482658293117931546 |
| dumpcap | 8473756179280619170 |
| evidence center | 3778500091710709090 |
| exeinfope | 8799118153397725683 |
| fakedns | 12027963942392743532 |
| fakenet | 576626207276463000 |
| ffdec | 7412338704062093516 |
| fiddler | 682250828679635420 |
| fileinsight | 13014156621614176974 |
| floss | 18150909006539876521 |
| gdb | 10336842116636872171 |
| hiew32 | 13260224381505715848 |
| unknown | 17956969551821596225 |
| hiew32demo | 12785322942775634499 |
| idaq64 | 8709004393777297355 |
| idaq | 14256853800858727521 |
| idr | 8129411991672431889 |
| ildasm | 15997665423159927228 |
| ilspy | 10829648878147112121 |
| jd-gui | 9149947745824492274 |
| lordpe | 3656637464651387014 |
| officemalscanner | 3575761800716667678 |
| ollydbg | 4501656691368064027 |
| pdfstreamdumper | 10296494671777307979 |
| pe-bear | 14630721578341374856 |
| pebrowse64 | 4088976323439621041 |
| peid | 9531326785919727076 |
| pe-sieve32 | 6461429591783621719 |
| pe-sieve64 | 6508141243778577344 |
| pestudio | 10235971842993272939 |
| peview | 2478231962306073784 |
| pexplorer | 9903758755917170407 |
| ppee | 14710585101020280896 |
| procdump64 | 13611814135072561278 |
| procdump | 2810460305047003196 |
| processhacker | 2032008861530788751 |
| procexp64 | 27407921587843457 |
| procexp | 6491986958834001955 |
| procmon | 2128122064571842954 |
| prodiscoverbasic | 10484659978517092504 |
| py2exedecompiler | 8478833628889826985 |
| r2agent | 10463926208560207521 |
| rabin2 | 7080175711202577138 |
| radare2 | 8697424601205169055 |
| ramcapture64 | 7775177810774851294 |
| ramcapture | 16130138450758310172 |
| reflector | 506634811745884560 |
| regmon | 18294908219222222902 |
| resourcehacker | 3588624367609827560 |
| retdec-ar-extractor | 9555688264681862794 |
| retdec-bin2llvmir | 5415426428750045503 |
| retdec-bin2pat | 3642525650883269872 |
| retdec-config | 13135068273077306806 |
| retdec-fileinfo | 3769837838875367802 |
| retdec-getsig | 191060519014405309 |
| retdec-idr2pat | 1682585410644922036 |
| retdec-llvmir2hll | 7878537243757499832 |
| retdec-macho-extractor | 13799353263187722717 |
| retdec-pat2yara | 1367627386496056834 |
| retdec-stacofin | 12574535824074203265 |
| retdec-unpacker | 16990567851129491937 |
| retdec-yarac | 8994091295115840290 |
| rundotnetdll | 13876356431472225791 |
| sbiesvc | 14968320160131875803 |
| scdbg | 14868920869169964081 |
| scylla_x64 | 106672141413120087 |
| scylla_x86 | 79089792725215063 |
| shellcode_launcher | 5614586596107908838 |
| solarwindsdiagnostics | 3869935012404164040 |
| sysmon64 | 3538022140597504361 |
| sysmon | 14111374107076822891 |
| task explorer | 7982848972385914508 |
| task explorer-x64 | 8760312338504300643 |
| tcpdump | 17351543633914244545 |
| tcpvcon | 7516148236133302073 |
| tcpview | 15114163911481793350 |
| vboxservice | 15457732070353984570 |
| win32_remote | 16292685861617888592 |
| win64_remotex64 | 10374841591685794123 |
| windbg | 3045986759481489935 |
| windump | 17109238199226571972 |
| winhex64 | 6827032273910657891 |
| winhex | 5945487981219695001 |
| winobj | 8052533790968282297 |
| wireshark | 17574002783607647274 |
| x32dbg | 3341747963119755850 |
| x64dbg | 14193859431895170587 |
| xwforensics | 17683972236092287897 |
| xwforensics64 | 17439059603042731363 |
Security Software Avoided
| Vendor | Process | FNV1A Hash |
|---|---|---|
| Panda | psanhost | 2532538262737333146 |
| psuaservice | 4454255944391929578 | |
| psuamain | 6088115528707848728 | |
| Kaspersky | avp | 13611051401579634621 |
| avpui | 18147627057830191163 | |
| ksde | 17633734304611248415 | |
| ksdeui | 13581776705111912829 | |
| Tanium | tanium | 7175363135479931834 |
| taniumclient | 3178468437029279937 | |
| taniumdetectengine | 13599785766252827703 | |
| taniumendpointindex | 6180361713414290679 | |
| taniumtracecli | 8612208440357175863 | |
| taniumtracewebsocketclient64 | 8408095252303317471 | |
| AVG/AVAST | aswidsagent | 2934149816356927366 |
| aswidsagenta | 13029357933491444455 | |
| aswengsrv | 6195833633417633900 | |
| avastavwrapper | 2760663353550280147 | |
| avgsvc | 3660705254426876796 | |
| avgui | 12709986806548166638 | |
| avgsvca | 3890794756780010537 | |
| avgidsagent | 2797129108883749491 | |
| avgsvcx | 3890769468012566366 | |
| avgwdsvcx | 14095938998438966337 | |
| avgadminclientservice | 11109294216876344399 | |
| afwserv | 1368907909245890092 | |
| avastui | 11818825521849580123 | |
| avastsvc | 8146185202538899243 | |
| bccavsvc | 16423314183614230717 |
Domains Avoided
| Domain | FNV1A Hash |
|---|---|
| swdev.local | 1109067043404435916 |
| swdev.dmz | 15267980678929160412 |
| lab.local | 8381292265993977266 |
| lab.na | 3796405623695665524 |
| emea.sales | 8727477769544302060 |
| cork.lab | 10734127004244879770 |
| dev.local | 11073283311104541690 |
| dmz.local | 4030236413975199654 |
| pci.local | 7701683279824397773 |
| saas.swi | 5132256620104998637 |
| lab.rio | 5942282052525294911 |
| lab.brno | 4578480846255629462 |
| apac.lab | 16858955978146406642 |
Service Disablement List
| Vendor | Process Names | Service Names |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Black | cavp | carbonblack |
| cb | carbonblackk | |
| cbcomms | ||
| cbstream | ||
| CrowdStrike | csfalconservice | csagent |
| csfalconcontainer | csdevicecontrol | |
| csfalconservice | ||
| FireEye | xagt | xagt |
| xagtnotif | fe_avk | |
| fekern | ||
| feelam | ||
| 3320767229281015341 (unknown) | ||
| ESET | ekrn | eamonm |
| eguiproxy | eelam | |
| egui | ehdrv | |
| ekrn | ||
| 2589926981877829912 (unknown) | ||
| epfwwfp | ||
| ekbdflt | ||
| epfw | ||
| F-Secure | fsgk32st | 17624147599670377042 (unknown) |
| fswebuid | 16066651430762394116 (unknown) | |
| fsgk32 | 13655261125244647696 (unknown) | |
| fsma32 | fsaua | |
| fssm32 | fsma | |
| fnrb32 | 3425260965299690882 (unknown) | |
| fsaua | fsbts | |
| fsorsp | fsni | |
| fsav32 | fsvista | |
| 13783346438774742614 (unknown) | ||
| 2380224015317016190 (unknown) | ||
| fses | ||
| fsfw | ||
| fsdfw | ||
| fsaus | ||
| fsms | ||
| fsdevcon | ||
| 14243671177281069512 (unknown) | ||
| 16112751343173365533 (unknown) |






We encourage you to share your thoughts on your favorite social platform.